Marburg virus disease is a highly infectious disease that causes haemorrhagic fever.
Okay.ng had reported earlier that the first case of it was confirmed in Guinea on Monday by the World Health Organisation.
Below are 10 key things to know about the disease:
1. Marburg virus is in the same family as the virus that causes Ebola and is transmitted in the same ways.
2. WHO says Marburg is transmitted to people from fruit bats and spreads among humans through direct contact with the bodily fluids of infected people, surfaces, and materials.
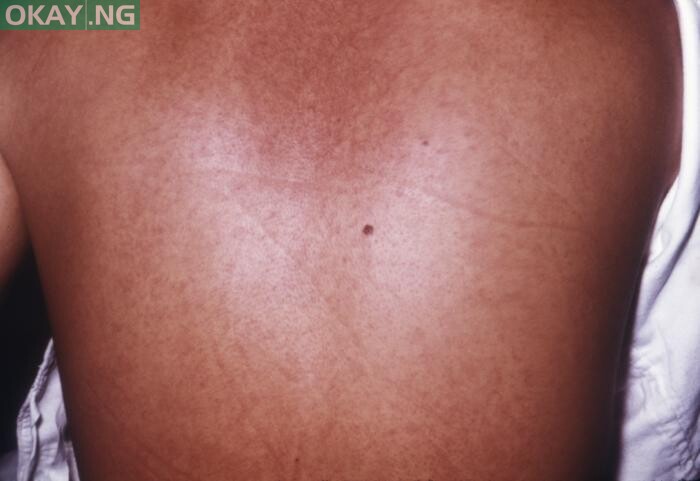
3. Symptoms include high fever, severe headache, and malaise. Many patients develop severe haemorrhagic signs within seven days.
4. The fatality case rates have varied from 24 per cent to 88 per cent in past outbreaks depending on virus strain and case management.
5. There are no vaccines or antiviral treatments approved to treat the virus.
6. However, supportive care in terms of rehydration with oral or intravenous fluids–and treatment of specific symptoms, improves survival.
7. Previous outbreaks in Africa have been reported in Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, South Africa, and Uganda.
8. The incubation period (interval from infection to onset of symptoms) for Marburg virus disease varies from 2 to 21 days.
9. It can be difficult to clinically distinguish Marburg virus disease from other infectious diseases such as malaria, typhoid fever, shigellosis, meningitis, and other viral haemorrhagic fevers
10. People remain infectious as long as their blood contains the virus.